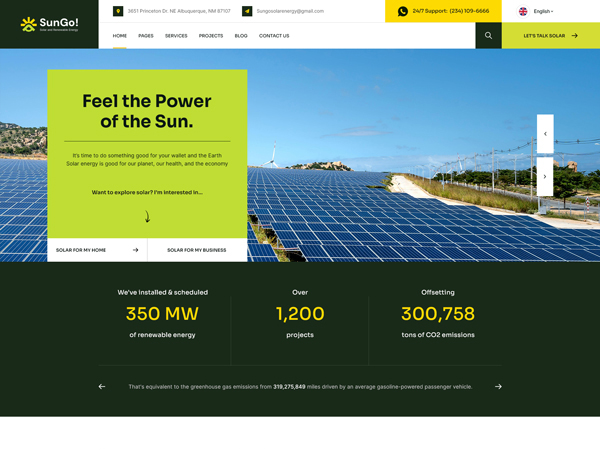
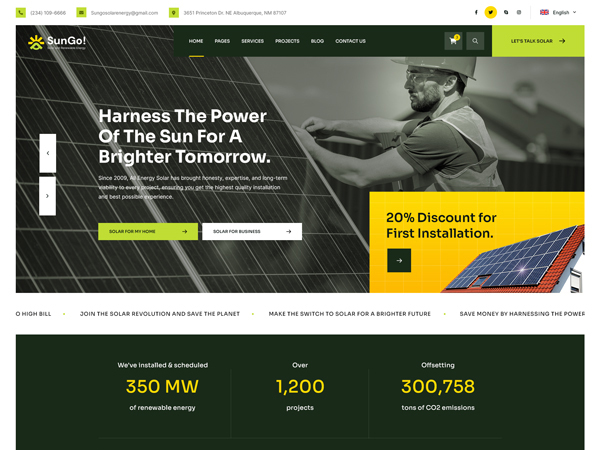
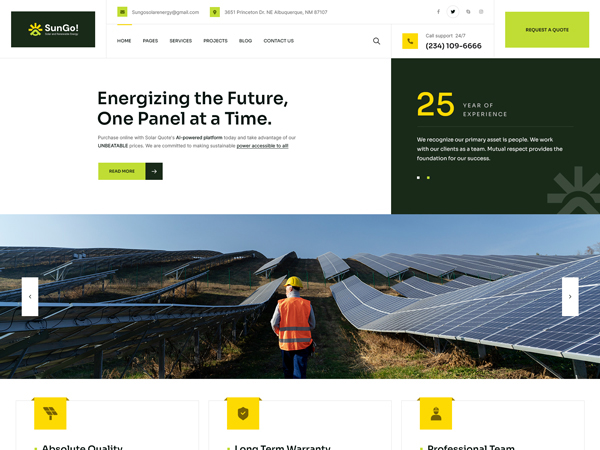
Solar power works by converting sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells, which are typically made of silicon. Here’s how the process works:
1. Sunlight Hits the Solar Panels
Solar panels are made up of many small units called solar cells. When sunlight strikes these cells, it excites the electrons in the silicon material, causing them to move. This movement generates an electric current.
2. Generation of Direct Current (DC)
The movement of electrons within the solar cells creates direct current (DC) electricity. However, most homes and businesses use alternating current (AC) electricity, so the DC needs to be converted.
3. Inverter Converts DC to AC
The DC electricity flows from the solar panels to an inverter, which changes the DC into AC electricity that can be used by your electrical appliances and fed into the power grid if there is excess production.
4. Electricity Distribution
The AC electricity is then distributed through your home’s electrical system, powering devices like lights, TVs, and refrigerators. Any extra electricity generated can either be stored in batteries or sent back to the grid (in the case of a grid-tied system), which can sometimes result in credits or payments for the excess energy.
5. Energy Storage (Optional)
In some setups, solar energy can be stored in batteries for use when the sun isn’t shining, such as at night or during cloudy days. These battery storage systems store the excess electricity produced by the solar panels during the day.
6. Grid Interaction (If Applicable)
If your system is connected to the grid, it can send unused electricity back to the grid, often through a process called net metering. In some cases, you can earn credits for the energy you contribute, reducing your utility bills.
Overall, the process takes the natural energy from the sun and turns it into a usable form of electricity, making it a renewable and sustainable source of power!